The journey to financial security often includes a pit stop at a common crossroad – the 401(k) plan. As I navigated my own path towards retirement, I discovered the profound impact this savings vehicle can have on one’s financial future. Let me guide you through the essentials of this retirement plan, its origin, and why it’s pivotal in mapping out your road to retirement.
Understanding the 401(k) Plan
A 401(k) plan, in its simplest form, is an employer-sponsored retirement savings plan that allows employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax salary towards long-term investments. This mechanism helps in accumulating substantial retirement funds, cushioned by tax benefits. It’s like building your own golden nest egg, chunk by chunk, while also enjoying immediate tax breaks. I fondly remember how I felt when I made my first contribution, knowing that I was not just saving money but actively investing in my future self.
The History and Origin of the 401(k)
Diving deeper into the origins of the 401(k), we need to go back to the late 1970s. The Revenue Act of 1978 included a provision that became Internal Revenue Code Sec. 401(k) (hence the name), allowing employees to avoid taxation on deferred compensation. However, it wasn’t until 1981 that the IRS officially sanctioned the use of these plans for retirement savings. Fast forward to today, and millions of Americans, like myself, use this powerful tool to bolster our retirement savings.
The Significance of the 401(k) in Retirement Planning
When I began my journey towards retirement planning, I quickly realized the immense value that various 401(k) plans can provide. Unlike traditional savings methods, the 401(k) comes with a significant advantage – the opportunity for tax-deferred growth. In layman’s terms, you won’t have to pay taxes on your savings until you withdraw them at retirement. This results in a more significant accumulation of funds, giving your nest egg the time and space it needs to grow.
Moreover, the 401(k) allows for higher annual contributions compared to other retirement plans. With higher contributions and compounded growth, the 401(k) sets the stage for substantial retirement savings. And if you’re fortunate like me, your employer might offer matching contributions, essentially offering free money towards your retirement.
Undeniably, understanding the 401(k) plan is the first step in taking control of your financial future. It is more than just a subsection of the tax code – it is a strategic instrument for securing your retirement.
As we move on to the next section, we will delve deeper into the mechanics of a 401(k) plan. We’ll unpack how your contributions are automatically deducted, the benefits of employer matching, and the updated contribution limits for 2023.
The Mechanism of a 401(k) Plan
Understanding the intricate workings of a 401(k) plan is like peeling an onion. Every layer reveals something unique and equally important. I have had my fair share of experience with this financial tool, and in this section, we will explore the gears that drive the 401(k) plan, including automatic paycheck deductions, the concept of employer matching, and the new contribution limits for 2023.
Understanding Automatic Deductions
One of the reasons I initially opted for a 401(k) was the seamless nature of contributions through automatic deductions. By signing up for a 401(k), a predetermined portion of your paycheck is automatically funneled into your retirement account before you even see it in your bank account. I still remember the relief I felt knowing that I was consistently contributing to my future, without having to move a finger or remember to transfer money each month.
The real beauty of this process lies in its simplicity and effectiveness. I fondly call it the ‘set it and forget it’ approach, a name I’m sure many finance enthusiasts would agree with. Not only does this strategy help build your savings effortlessly, but it also reduces your taxable income since the deductions are made pre-tax.
The Power of Employer Matching
If there’s one feature of 401(k) plans that adds a significant boost to retirement savings, it’s employer matching. Employer matching is when your employer contributes to your 401(k) plan, matching your own contributions up to a certain limit. To put it simply, it’s like receiving free money towards your retirement savings. The memory of my first matching contribution is still clear in my mind, and the profound impact it had on my savings growth was unparalleled.
However, not all employers offer matching contributions, and those that do often have a vesting schedule, which means you earn the right to your employer’s contributions over a set period of employment. Therefore, it’s crucial to understand your employer’s policy to fully benefit from this feature.
Annual Contribution Limits for 2023
The annual contribution limit for a 401(k) plan is the maximum amount you can contribute each year, and it’s subject to change. In 2023, the limit has increased to $22,500, up from $20,500 in 2022. For those aged 50 and above, like myself, there’s a special provision called ‘catch-up contributions,’ which allows for an even higher limit, set at $30,000 in 2023.
It’s crucial to stay updated with these changes, as they directly impact your retirement savings strategy. Remember, the more you contribute (up to the limit), the larger your nest egg will grow, courtesy of compound interest.
Exploring the nuts and bolts of a 401(k) plan offers an appreciation for its benefits and the power it can lend to your retirement savings strategy. As we progress to our next segment, we will navigate the labyrinth of different types of 401(k) plans and their unique features. We’ll compare the Traditional 401(k) to the Roth 401(k), explaining the tax benefits associated with each and why one might be more advantageous for your retirement goals.
Types of 401(k) Plans and Their Distinctions
Deciding between the two primary types of 401(k) plans, the Traditional 401(k) and the Roth 401(k), is akin to a balancing act. Each option comes with its own set of benefits, and the choice can significantly impact your future financial situation. My own journey of retirement planning led me to understand these distinctions, and I’m here to help you navigate through them.
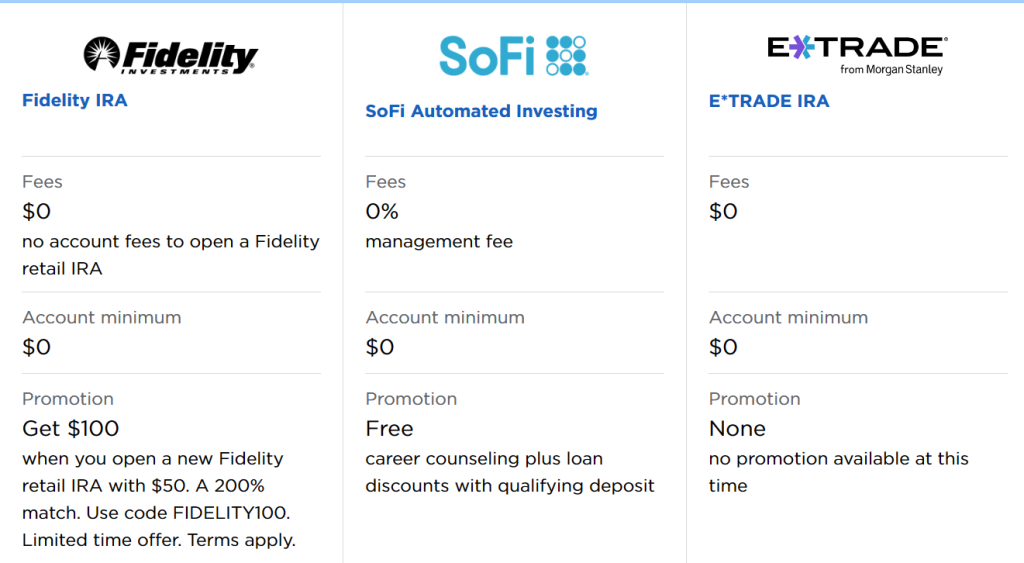
Traditional 401(k) Vs. Roth 401(k): A Detailed Comparison
Choosing between a Traditional 401(k) and a Roth 401(k) can be daunting. When I was making this choice, I had to consider my current financial situation, tax implications, and my projected income during retirement.
A Traditional 401(k) plan, which I first opted for early in my career, offers pre-tax contributions. This means that the money is deducted from your paycheck before taxes, effectively reducing your taxable income. The funds then grow tax-free over the years until retirement, when withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income.
On the other hand, Roth 401(k) contributions are made post-tax. I remember the year I switched to a Roth 401(k), thinking of the tax-free withdrawals I would enjoy during retirement. The taxes are paid upfront, which means that the contributions do not reduce your current taxable income. However, the trade-off is that the withdrawals during retirement are tax-free, provided certain conditions are met.
Unraveling the Tax Benefits
When we discuss tax benefits, both types of 401(k) plans offer advantages, but at different stages. The Traditional 401(k)’s upfront tax break can be a boon, especially if you’re in a high tax bracket now and anticipate being in a lower one at retirement. I recall my early years, juggling student loans and rent; the tax savings from my Traditional 401(k) contributions were a welcome relief.
Conversely, a Roth 401(k) provides tax-free growth and withdrawals, making it a beneficial option if you anticipate being in a higher tax bracket during retirement. Given the trajectory of my career and the possibility of increased taxes in the future, transitioning to a Roth 401(k) was a strategic decision for me.
Spotlight on Roth 401(k) and Future Withdrawals
The beauty of a Roth 401(k) truly shines through when you consider future withdrawals. Imagining my retirement years, I found comfort knowing that every dollar I withdraw from my Roth 401(k) would be mine to keep, with Uncle Sam having no claim on it.
Roth 401(k) plans promise tax-free withdrawals during retirement, giving you a clear picture of your available funds. This certainty can be a significant advantage when planning your retirement expenses.
Having explored the ins and outs of Traditional and Roth 401(k) plans, it’s evident that the choice between them depends on your unique financial situation and future expectations. But the world of retirement planning does not end here. As we delve into the next segment, we’ll discuss new changes and developments in 401(k) plans, including increased contribution limits, automatic enrolment rules, and the portability of a 401(k). These updates have the potential to influence your retirement savings strategy, so stay tuned.
New Changes and Developments in 401(k) Plans
As an individual keenly interested in my retirement savings and financial future, I keep a close watch on any new developments and changes in 401(k) plans. Over time, I’ve realized that these changes can greatly impact the value of our retirement nest eggs and the strategies we employ to grow them. Today, I will share my insights on the recent changes that have happened in the 401(k) landscape.
Increased Contribution Limits Due to Inflation
In 2023, I was pleasantly surprised when the IRS announced a bump in the annual contribution limits for 401(k) plans due to inflation. The limit was raised from $19,500 to $20,500 for individuals below 50, allowing us to put away an additional $1,000 towards our golden years. The catch-up contribution limit for those aged 50 and above remained at $6,500, bringing their total contribution limit to $27,000.
This might seem like a small change, but over the years, I’ve learned that even small increments can have a significant impact on the final corpus, thanks to the magic of compounding. So, this is a welcome development for all of us looking to maximize our retirement savings.
Automatic Enrolment Rules Starting 2025
Another notable change is the automatic enrolment feature that employers will need to incorporate starting 2025. Automatic enrolment in a 401(k) plan means that as soon as you are eligible, you are automatically enrolled in the company’s 401(k) plan unless you specifically choose to opt out.
I recall my early career days when I was not as financially savvy. If my employer had an automatic enrolment rule, I would have started contributing to my 401(k) much sooner. I believe this rule will be instrumental in getting more people to start saving for retirement early in their careers, thereby reaping the benefits of compounding over a longer time horizon.
Portability of a 401(k) and the Process of Rolling Over to an IRA
Finally, one of the most significant developments in recent years has been the increased emphasis on the portability of a 401(k). As a professional who has changed jobs a few times, I understand the importance of this feature. Essentially, it allows you to move your 401(k) funds when you change jobs without any tax implications.
One popular method of doing this is by rolling over to an Individual Retirement Account (IRA). The process is quite straightforward. Upon leaving a job, you can choose to roll over your 401(k) balance into an IRA, thereby continuing to enjoy tax-deferred growth. During my last job transition, this rollover allowed me to consolidate my retirement savings and manage them efficiently.
Having taken a look at the recent changes and developments in 401(k) plans, it’s clear that staying abreast of these updates is crucial for effective retirement planning. In the next segment, we will explore an important alternative and complement to 401(k) plans – the Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs). We will discuss their benefits, the comparison between 401(k) plans and IRAs, and how you can leverage both to optimize your retirement savings. So, stay tuned for a deep dive into the world of IRAs.
Alternatives and Complements to 401(k) Plans: IRAs
When it comes to retirement savings, my journey has taught me that it’s wise not to put all eggs in one basket. This is where the Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) come into play. IRAs can serve as excellent alternatives or complements to 401(k) plans, allowing us to diversify our retirement savings strategy. Today, I’ll share my understanding of IRAs and how to make the most of them along with your 401(k) plan.
Introduction to Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
IRAs, like 401(k) plans, are tax-advantaged retirement accounts. However, unlike 401(k) plans, which are offered by employers, anyone with earned income can open an IRA. I have found that having an IRA gives me more control over my retirement savings as I get to choose the financial institution, the investments, and the frequency of my contributions.
Comparison between 401(k) Plans and IRAs: Pros and Cons
When I first explored IRAs, I found it helpful to compare them to 401(k) plans. Both types of accounts offer tax advantages, but they differ in a few key areas.
One of the main advantages of 401(k) plans is the potential for employer matching contributions, which can significantly boost your savings. On the other hand, IRAs often provide a wider array of investment options, allowing for a more tailored investment strategy.
However, there are contribution limit differences as well. While the 401(k) has a relatively higher limit, IRAs limits are considerably lower. But, depending on your income and tax filing status, the contributions you make to a Traditional IRA might be tax-deductible.
Leveraging Both 401(k) Plans and IRAs for Retirement Savings
After understanding the distinctions, I learned to leverage both 401(k) plans and IRAs to maximize my retirement savings. I initially started with contributing enough to my 401(k) to get the full employer match, essentially free money. Then, I would contribute to an IRA for additional savings and more investment options.
Combining these strategies has allowed me to take full advantage of the tax benefits of both accounts and also diversify my investment portfolio, adding a layer of security to my retirement savings.
Recap and Conclusion
Having journeyed through the intricacies of 401(k) plans and IRAs, I hope these insights have empowered you to make more informed decisions about your retirement savings.
We started with the basics of a 401(k) plan, understanding its definition, history, and significance in retirement planning. We then dived into the mechanisms of a 401(k), with a focus on the automatic deductions, employer matching, and contribution limits.
Following that, we explored the different types of 401(k) plans and their unique tax benefits, particularly highlighting the advantages of Roth 401(k) for future withdrawals. We also examined the recent changes and developments in 401(k) plans, such as increased contribution limits, automatic enrollment rules, and the portability of a 401(k) plan.
Finally, we broadened our retirement savings strategy by considering the Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs), comparing them to 401(k) plans and learning how to leverage both for maximum benefit.
Planning for retirement might seem complex, but remember, every journey begins with a single step. Whether it’s starting with your first 401(k) contribution or opening an IRA, each step you take brings you closer to a secure and comfortable retirement.
Q1: What is a 401(k) plan and why is it essential for retirement planning?
A: A 401(k) plan is a tax-advantaged retirement savings plan offered by employers. It plays a crucial role in retirement planning as it allows employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax earnings, thereby encouraging savings for the future while reducing the current taxable income.
Q2: How does a 401(k) plan work?
A: A 401(k) plan works through automatic deductions from your paycheck. These deductions are pre-tax, which means they reduce your taxable income. Moreover, some employers may offer matching contributions up to a certain percentage, further enhancing your retirement savings.
Q3: What are the differences between a Traditional 401(k) and a Roth 401(k)?
A: A Traditional 401(k) allows for pre-tax contributions, which grow tax-free until withdrawal during retirement, at which point they are taxed as ordinary income. In contrast, Roth 401(k) contributions are made with post-tax dollars, but both the contributions and earnings can be withdrawn tax-free in retirement, subject to certain conditions.
Q4: What are the new developments in 401(k) plans?
A: Some of the recent developments include an increase in contribution limits due to inflation. Additionally, starting 2025, new rules regarding automatic enrollment by employers are set to be implemented. Also, the portability of 401(k) plans has improved with more straightforward processes for rolling over to an IRA.
Q5: What is an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) and how does it compare with a 401(k) plan?
A: An IRA is another type of tax-advantaged retirement account that individuals can open independently. It offers more investment options compared to a 401(k) plan. However, the contribution limits are typically lower. Both 401(k) plans and IRAs can be essential parts of a comprehensive retirement strategy, and it’s often beneficial to utilize both.
Leave a Reply